Many diseases harm the human body. Among these diseases, the most common ones are auto-immune and sexually transmitted diseases. Sexually transmitted diseases are not spread through any virus or bacteria present in the atmosphere. These are transmitted from one person to the other through physical and intimate contact.
However, these diseases if not diagnosed or treated on time can be fatal for the patient. Many diseases fall into the category of sexually transmitted diseases.
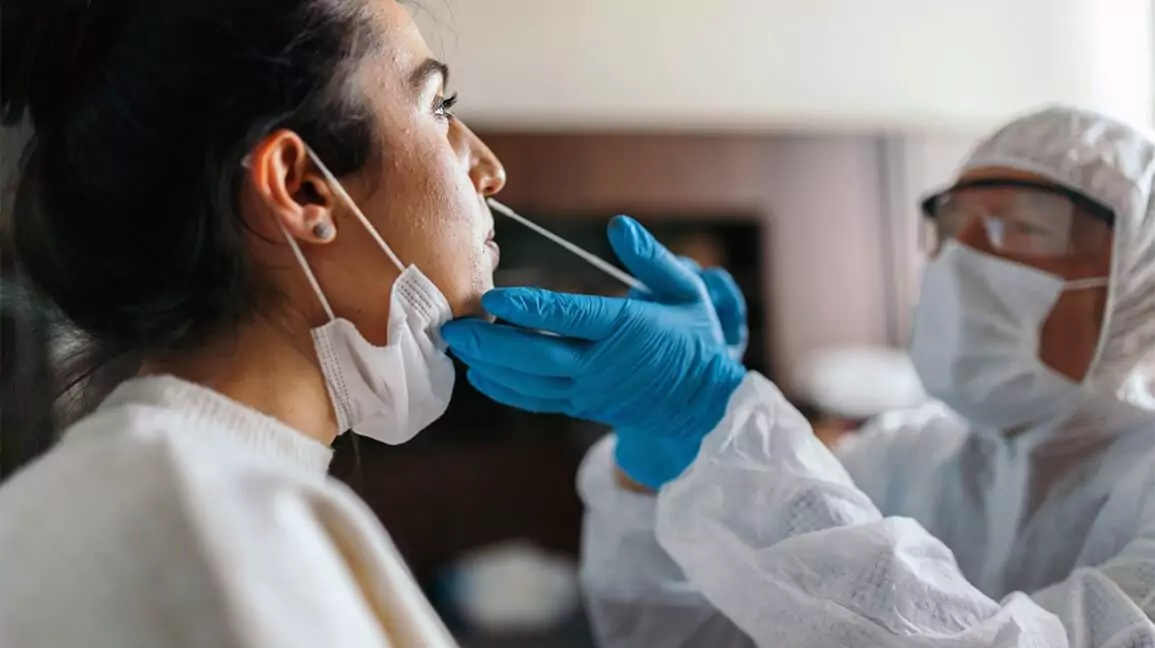
STDs used to be called venereal conditions or VD. They’re among the most common contagious conditions. It’s estimated that 25 of all Americans have an incorrigible STD. Each time, 20 million new cases are reported; half of these infections are among people periods 15 to 24 and they can have long-term consequences. HIV test in UAE and USA can be easily conducted.
STDs are serious ails that bear treatment. Some STDs, similar to HIV, can not be cured and can be deadly. By learning further about STDs, you can learn ways to cover yourself. STD testing is not difficult anymore. Normally, full sexual health screening is required to discover the actual cause of HIV.
You can get an STD from vaginal, anal, or oral coitus. You can also be infected with trichomoniasis through contact with damp or wettish objects similar as apkins, wet apparel, or restroom seats, although it’s further generally spread by sexual contact.
With the preface of largely active antiretroviral remedies, AIDS judgments and deaths declined mainly in the United States from 1995 to 1998 and remained stable from 1999 to 2008 at a normal of AIDS judgments and deaths per time, independently. Despite the decline in AIDS cases and deaths, at the end of 2008, estimated persons were living with HIV, including (20.1) whose infection remains undiagnosed. In particular, the undiagnosed HIV infections leave the sexual mates of these persons at high threat of infection.
Mortal Immunodeficiency Contagion (HIV) and Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
AIDS is caused by the mortal immunodeficiency contagion (HIV), which is spread through vulnerable sexual intercourse with an infected person or through using a polluted needle to fit medicines. It can also be spread through intravenous medicine use and much lower generally, blood, blood products, needles, or other sharp instruments defiled with infected body fluids or blood.
Upon entering the rotation, the HIV microorganisms abduct a type of white blood cell known as T- coadjutor lymphocytes ( also known as CD4 cells, T cells, or coadjutor-Ts). In a person with a healthy vulnerable system, T- cells band together to help defend the body against conditions. But the commandeered T- cells are forced to mass-produce clones of HIV. Left undressed, coadjutor T cells mass-produce large figures of HIV, this further depletes the number of normal coadjutor-Ts in the bloodstream, rendering the individual vulnerable to AIDS-defining illness.
The five most common of these are
- Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
- HIV wasting pattern
- Candidiasis of the esophagus
- Tuberculosis
- Kaposi’s sarcoma
to order one for you. Some health departments or community-grounded associations also give tone-test accouterments for free.

Some prominent symptoms of HIV
There are several symptoms of HIV. Not everyone will have the same symptoms. It depends on the person and what stage of the complaint they’re in. Below are the three stages of HIV and some of the symptoms people may witness.
- Stage 1 Acute HIV Infection
Within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV, about two-thirds of people will have a flu-suchlike illness. This is the body’s natural response to HIV infection.
Flu-suchlike symptoms can include
- Fever
- Chills
- Rash
- Night sweats
- Muscle Pangs
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Blown lymph bumps
- Mouth ulcers
These symptoms can last anywhere from many days to several weeks. But some people don’t have any symptoms at each during this early stage of HIV.
Get tested as soon as possible! Find an HIV testing point near youLocator.HIV.gov Don’t assume you have HIV just because you have any of these symptoms — they can be analogous to those caused by other ails. But if you suppose you may have been exposed to HIV, get an HIV test.
Here’s What To Do
Find an HIV testing point near you — You can get an HIV test at your primary care provider’s office, your original health department, a health clinic, or numerous other places. Use the HIV Services Locator to find an HIV testing point near you.
Request an HIV test for recent infection — Utmost HIV tests descry antibodies (proteins your body makes as a response to HIV), not HIV itself. But it can take many weeks after you’re infected for your body to produce them. Other types of tests can descry HIV infection sooner. Tell your croaker or clinic if you suppose you were lately exposed to HIV, and ask if their tests can descry early infection.
Know your status — After you get tested, be sure to learn your test results. However, see a croaker as soon as possible so you can start treatment with an HIV drug If you’re HIV-positive. And be apprehensive when you’re in the early stage of infection, you’re at veritably high threat of transmitting HIV to others. It’s important to take away to reduce your threat of transmission. However, there are forestallment tools like exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) that can help you stay negative If you’re HIV-negative.
Stage 2 Clinical Quiescence
In this stage, the contagion still multiplies, but in veritably low situations. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called habitual HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage 10 or 15 times, but some move through this stage briskly.
Still, exactly as specified and get and keep an undetectable viral cargo, you can cover your health and have effectively no threat of transmitting HIV to your sexual mate (s), If you take HIV drug every day.
But if your viral cargo is sensible, you can transmit HIV during this stage, indeed when you have no symptoms. It’s important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral cargo checked.
Stage 3 AIDS
Still, ultimately the contagion will weaken your body’s vulnerable system and you’ll progress to AIDS ( acquired immunodeficiency pattern) If you have HIV and you aren’t on HIV treatment. This is the late stage of HIV infection.

Symptoms of AIDS can include
- Rapid weight loss
- Recreating fever or gushing night sweats
- Extreme and unexplained frazzle
- Dragged lump of the lymph glands in the armpits, groin, or neck
- Diarrhea that lasts for further than a week
- Blisters of the mouth, anus, or genital
- Pneumonia
- Red, brown, pink, or purplish blotches on or under the skin or inside the mouth, nose, or eyelids
- Memory loss, depression, and other neurologic diseases
Each of these symptoms can also be related to other ails. The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. However, a health care provider will diagnose if your HIV has progressed to carry 3 (AIDS) grounded on certain medical criteria If you’re HIV-positive.
Numerous of the severe symptoms and ails of HIV complaint come from the opportunistic infections that do because your body’s vulnerable system has been damaged. See your health care provider if you’re passing any of these symptoms.